Signaalilinjat ja voimajohdot ovat kaksi avainlinjaa elektronisissa järjestelmissä, jotka ovat toisistaan riippuvaisia ja joilla on selkeä työvoima. Niiden suhde voidaan analysoida seuraavista viidestä ulottuvuudesta:
Virranjohdot:
Tarkoitus: Sähkövirran toimittaminen laitteelle, antaa sen toimia.
Keskittyä: Ensisijaisesti jännitteen pudotus, lämmön hajoaminen, ja varmistaa turvallinen ja luotettava polku nykyiselle virtaukselle.
Koko: Saattaa joutua olemaan suurempi ja muotoiltu erityisesti korkeille virtauksille ja lämmön hallitsemiseksi.
Esimerkit: Johdot kotitalouspiirissä tai johdot, jotka kuljettavat virtaa tietokoneeseen.
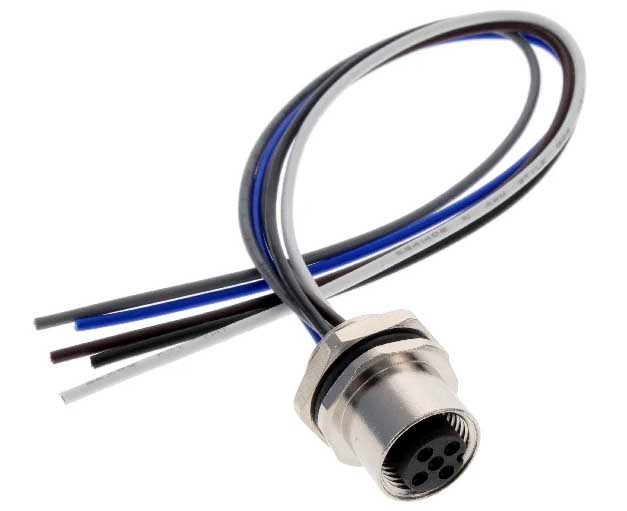

T4171310005-001 2 x -signaali + Virtajohto 1.5 MM2 -kokoonpano
Signaalijohdot:
Tarkoitus:
Sähkösignaalien tai tietojen lähettäminen laitteiden välillä.
Keskittyä:
Huolissaan signaalin eheydestä, minimointi kohinan ja häiriöiden minimointi, ja tietojen tarkan siirron varmistaminen.
Muotoilu ja muotoilu:
Saattaa joutua suunnittelemaan ylläpitämään tasaisia sähköominaisuuksia ja minimoimaan signaalin vääristymisen, etenkin korkeammilla taajuuksilla tai pidemmillä etäisyyksillä.
1. Toiminnallinen täydentävä suhde
Signal Line: Kuljettaa pienitehoisia tiedonsiirtoa, mukaan lukien ohjaussignaalit, analogiset/digitaaliset signaalit (kuten ääni, video, anturitiedot), on herkkä sähkömagneettisille häiriöille ja sen on varmistettava signaalin eheys.
Power Line: on suunniteltu tarjoamaan voimaa laitteille, välittää suuritehovirtaa (muutamasta watista megawatteihin), ja sen on varmistettava jännitteen ja virran vakaus laitteiden käytön ylläpitämiseksi.
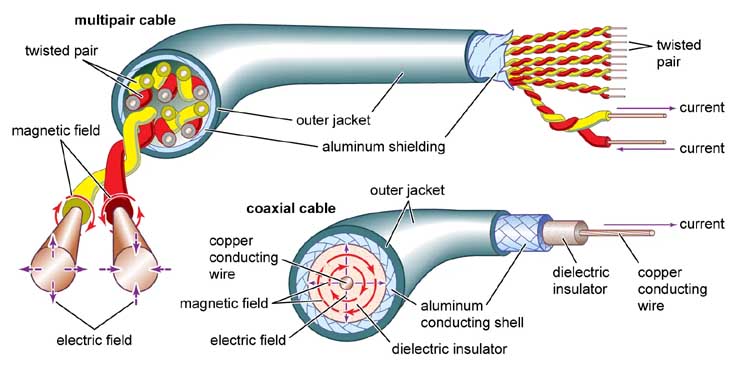
Signaalikaapeli ja erot ohjauskaapeleista
2. Fyysiset rakenneerot
Juohja- ja suoja -suunnittelu:
Signaalilinjat käyttävät usein moniytimistä kierrettyjä johtoja tai koaksiaalikaapeleita, Jotkut metallien suojakerroksissa häiriöiden tukahduttamiseksi (kuten RVVP -johdot).
Voimajohdot ovat pääosin kuparin kapellimestareita, yksinkertaisilla rakenteilla, mutta suurilla poikkileikkausalueilla. Joidenkin korkeajännitevirtalinjojen on läpäistävä turvallisuussertifikaatti.
Tyyppiset tyypit:
Signaaliviivat: kierretty pari (häiriön vastainen suorituskyky liittyy kiertymisetäisyyteen), optinen kuitu (ei-metallinen kantaja).
Voimajohto: Yleinen kumimuovijohto (kestävä), pehmeät voimalinjat (Sovellettavissa kodinkoneisiin).
3. Lähetysominaisuudet ja häiriöiden suojaus
OLTONE/Power Range:
Signaalilinja: Jännite on yleensä muutama voltti kymmeniin voltteihin, ja voima on milliwattitasolla.
Sähköjohto: Jännite voi saavuttaa kilovolit, ja voima peittää Wattsin megawatteihin.
Anti-häiriömittaukset:
Signaalilinjat on ohjattava pois sähkölinjoista, ja suojaus- ja maaverkon eristämistä käytetään (kuten digitaalisen maan ja analogisen maan erottaminen piirilevyssä).
Power Line käyttää katkaisukondensaattoreita (Chip -kondensaattorit on asennettu lähelle) ja leveä maadalangan suunnittelu silmukan häiriöiden vähentämiseksi.
4. Järjestelmän asettelun koordinointi
PCB -suunnittelusäännöt:
Voimajohto ja pohjaviiva muodostavat suljetun silmukan reitityksen välttämiseksi; Digitaalinen piiri ottaa käyttöön a “hyvin”-muotoinen jauhettu ruudukon asettelu.
Signaalilinja noudattaa lyhyintä polun periaatetta, ja herkkä signaalialue välttää päällekkäisyydet sähkökerroksen kanssa.
Connector -sopeutuminen:
Sekavaihteistoissa, Signaalien kanssa yhteensopivat monitoimiset liittimet ja virran tulisi valita rajapintojen lukumäärän vähentämiseksi.
5. Vaihdettavuus rajoitetuissa olosuhteissa
Tietyissä skenaarioissa, Signaalilinjat voivat väliaikaisesti korvata sähkölinjat teknisen muunnoksen kautta, esimerkiksi:
PoE -virtalähde: Ethernet -kierretyt parikaapelit lähettävät tietoja ja virtaa samanaikaisesti, mutta niitä rajoittavat voima ja etäisyys.
Adapter : Esimerkiksi, Videon signaalikaapelit on saatettava virtalähteenä kierrettyjen parien lähettimien avulla.
Kuitenkin, tavanomaisissa hakemuksissa, Nämä kaksi eivät ole vaihdettavissa johtuen kantokyvyn ja häiriöiden vastaisten vaatimusten eroista.
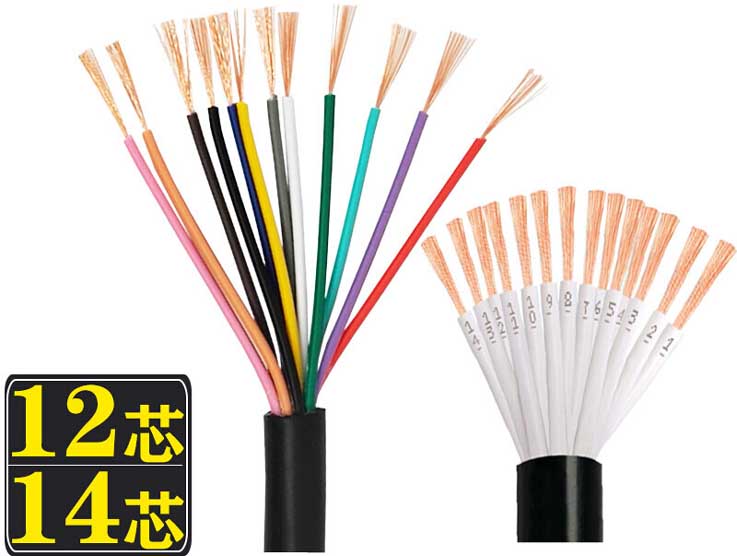

Kuparin ytimen virtajohto, signaalin ohjauskaapeli RVV12 -ydin 14 ydin
Johtosarja koostuu kahdesta elementistä: johdot (signaalijohdot, virranjohdot) ja liittimet.
Elektronisten komponenttien lisäksi, Lankaharjat ovat myös välttämättömiä elektronisissa tuotteissa. Vaikka monet tuotteet käyttävät levylle ja aloitteisiin liittimiin johtimien sijasta, Suurinta osaa elektronisista laitteista ei vieläkään voida erottaa johtosarjoista signaalin ja voimansiirron suhteen. Lankaharja koostuu yleensä johdoista, liittimet, takki, tai eristys. Yaxun -elektronisten liittimien toimittaja keskustelee kanssasi signaalilinjojen välisistä suhteista, kytkentäjohdot ja liittimet johtosarjassa.
Kuten nimi ehdottaa, Signaalilinjat viittaavat pääasiassa linjoihin, joita käytetään tunnistustietojen ja ohjaustietojen lähettämiseen sähköohjauspiireissä. Signaalilinjat koostuvat yleensä useista kaapeleista, jotka muodostavat yhden tai useamman lähetyslinjan, tai ne voidaan myös tulostaa piirejä, jotka on järjestetty painettuun piirilevyyn. Tieteen jatkuvan etenemisen myötä, tekniikka ja sovellukset, Signaalilinjat ovat kehittyneet metallikuljettajista muihin lentoliikenteen harjoittajiin, kuten optiset kaapelit. Standardisoidun tuotannon ja sovelluksen helpottamiseksi, Signaalilinjat eri tarkoituksiin on yleensä erilaisia teollisuusstandardeja.
Power Lines ovat johtoja, jotka kuljettavat sähkövirtaa. Tyypillisesti, Pisteestä pisteeseen on kuinka sähkö siirretään. Virtajohdot voidaan jakaa tasavirtajohtoihin ja vaihtovirtajohtoihin niiden käyttötarkoituksen mukaan. Yleensä, AC-virtajohdot ovat johtoja, jotka ohittavat korkeajännitteen vuorottelevan virran. Korkean jännitteen vuoksi, Tämän tyyppistä johtoa ei voida virallisesti tuottaa, ennen kuin se saa turvallisuussertifikaatin yhtenäisten standardien mukaisesti. DC -tasavirtaviivat kulkevat periaatteessa alemman jännitteen tasavirtalähteen läpi, Joten turvallisuusvaatimukset eivät ole yhtä tiukkoja kuin vaihtovirtalinjat. Kuitenkin, turvallisuussyistä, Maat tarvitsevat edelleen yhtenäistä turvallisuussertifiointia.
Suuri ero signaalilinjojen ja tehoviivojen välillä on, että signaalilinjat lähettävät analogisia signaaleja tai digitaalisia signaaleja, ja virtajohtoja käytetään virran lähettämiseen. Signaalilinjat viittaavat viivoihin, jotka lähettävät tietoja, ja sähköjohdot viittaavat piireihin, jotka tarjoavat virtaa. Itse asiassa, Sähkösignaalit käyvät myös signaalilinjoissa, jotka ovat vain säännöllisiä, järjestetty, ja tiedonkantavat sähkösignaalit. Virtajohto kantaa vain tasavirta -virtaa kiinteällä jännitearvolla. Elektronisesti, liittimet toimivat aiheuttamatta signaalin imeytymistä, vaimennus, ja virranhäviö järjestelmän suorituskyvylle. Se tarjoaa myös irrotettavia yhteyslaitteita elektronisten järjestelmien välillä. Siksi, Niiden välillä tarvitaan lanka.
Signaaliviivat, voimajohto, ja liittimet voivat olla olemassa itsenäisesti tai rinnakkain. Jos elektronisissa tuotteissa on signaali- ja tehonsiirtovaatimuksia, Kuinka liittimiä voi olla vähemmän? Siksi, Nämä kolme ovat toisistaan riippuvaisia ja rinnakkain, ja ovat välttämättömiä elektronisissa tuotteissa.
Yllä oleva toimittaja jakoi, Toivon, että siitä on apua kaikille. Yaxun Electronics tarjoaa integroidun r&D ja tuotantopalvelut tuotteiden muovi- ja laitteistopäätteiden muottien kehittämisestä, tarkkuus muovinen ruiskuvalu, Tarkkuuslaitteistojen nopea leimaus, terminaali, ja autovaljaiden automatisoitu kokoonpano. Jos tarvitset yksityiskohtaisempia tietoja, Voit ottaa yhteyttä henkilökuntaan kuulemista varten.
 English
English العربية
العربية bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά עברית
עברית Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska தமிழ்
தமிழ் ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
